SEO: Your Comprehensive Guide to Boosting Search Engine Optimization Rankings
Introduction to SEO: Why Engine Optimization Matters
In today’s digital landscape, having a fantastic website isn’t enough if nobody can find it. This is where SEO (Search Engine Optimization) comes into play. SEO is the practice of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website through organic search engine results. Essentially, it’s about making your website more visible to people who are looking for what you offer via search engines like Google.
This guide will break down the core components of SEO and show you exactly how to implement effective strategies for superior engine optimization to boost your engine rankings.
How to Master SEO: Essential Pillars for Success
1. On-Page SEO: Optimizing Your Content and Strategy
On-page SEO refers to all the measures you can take directly within your website to improve its position in search rankings. This is where detailed SEO strategy is executed.
How to Optimize Titles and Meta Descriptions: Your title tag is the first thing users see in search results. It should be compelling, contain your primary keyword, and accurately describe the page’s content. For WordPress users, dedicated seo tools like Yoast SEO provide a preview and a crucial content analysis for ensuring the focus keyword is used optimally in these areas.
How to Use Keywords Effectively: Keywords are the words and phrases people type into search engines. Once identified, integrate them naturally into your content, headings (H1, H2, H3), and image alt text. Avoid “keyword stuffing,” which can harm your rankings.
How to Create High-Quality SEO Content: Content is king in SEO. Your seo content should be original, valuable, comprehensive, and engaging. Focus on answering user queries and providing in-depth information. Tools like Surfer and Moz can help ensure your content is fully optimized against competitive pages.
2. Off-Page SEO: Building Authority Outside Your Site
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your own domain to impact your engine rankings within SERPs. The most prominent factor is backlinks, which build authority.
How to Build High-Quality Link Authority: Backlinks act as “votes of confidence.” Focus on earning links from authoritative, relevant websites. SEO tools like Ahrefs and Semrush are essential for analyzing competitor link profiles to uncover opportunities.
How to Leverage Social Media: Social media amplifies your seo content, drives traffic to your site, and increases brand visibility, which can indirectly lead to more link opportunities and mentions.
How to Get Local Citations: For local SEO, ensuring your business information (NAP) is consistent across online services and directories is crucial.
3. Technical SEO: Ensuring Search Engine Friendliness
Technical SEO involves optimizing the infrastructure of your website to help search engine crawlers efficiently crawl and index your site. This is a primary function of good engine optimization.
How to Improve Site Speed: Page load speed is a critical ranking factor. Use a CDN, compress images, and minimize code. A dedicated SEO specialist may use tools like Screaming Frog for in-depth technical audits.
How to Ensure Mobile-Friendliness: With mobile-first indexing, a responsive and mobile-friendly website is non-negotiable for all search engines.
How to Structure Your Site (Crawlability & Indexability): Use an XML sitemap and a robots.txt file to instruct crawlers. Yoast SEO and other WordPress SEO plugins often automate the creation and submission of these files.
The Role of Yoast SEO in WordPress Optimization
For those running sites on the WordPress CMS, leveraging a specialized seo tool like Yoast SEO is a fundamental step in engine optimization.
Real-time Content Analysis: Yoast SEO provides immediate feedback on your content readability and on-page SEO health, guiding you to naturally integrate your focus keyword into your copy, headings, and meta-data.
Schema Markup & Technical Settings: It automatically handles complex technical aspects like generating correct Schema markup and configuring your robots.txt and sitemaps, making complex SEO technology accessible.
4. Monitoring and Analytics: Tracking Your SEO Progress
SEO is an ongoing process—a marathon of continuous search engine optimization. Regular monitoring helps you understand what’s working and what needs adjustment to maintain high engine rankings.
How to Use Google Analytics: Google Analytics provides insights into organic search traffic, user behavior, and conversion rates, allowing you to gauge the success of your seo strategy.
How to Use Google Search Console: Google Search Console shows your site’s performance directly in Google Search results. It identifies crawling errors, security issues, and provides crucial keyword performance data—essential for any SEO specialist.
Conclusion
Mastering SEO is a marathon, not a sprint. By consistently applying these “how to” strategies across on-page, off-page, and technical aspects, leveraging powerful seo tools like Yoast SEO and Semrush, and continuously analyzing your performance, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility and drive sustainable organic traffic. Stay updated with algorithm changes and continuously analyze your performance to stay ahead in the competitive search marketing landscape.
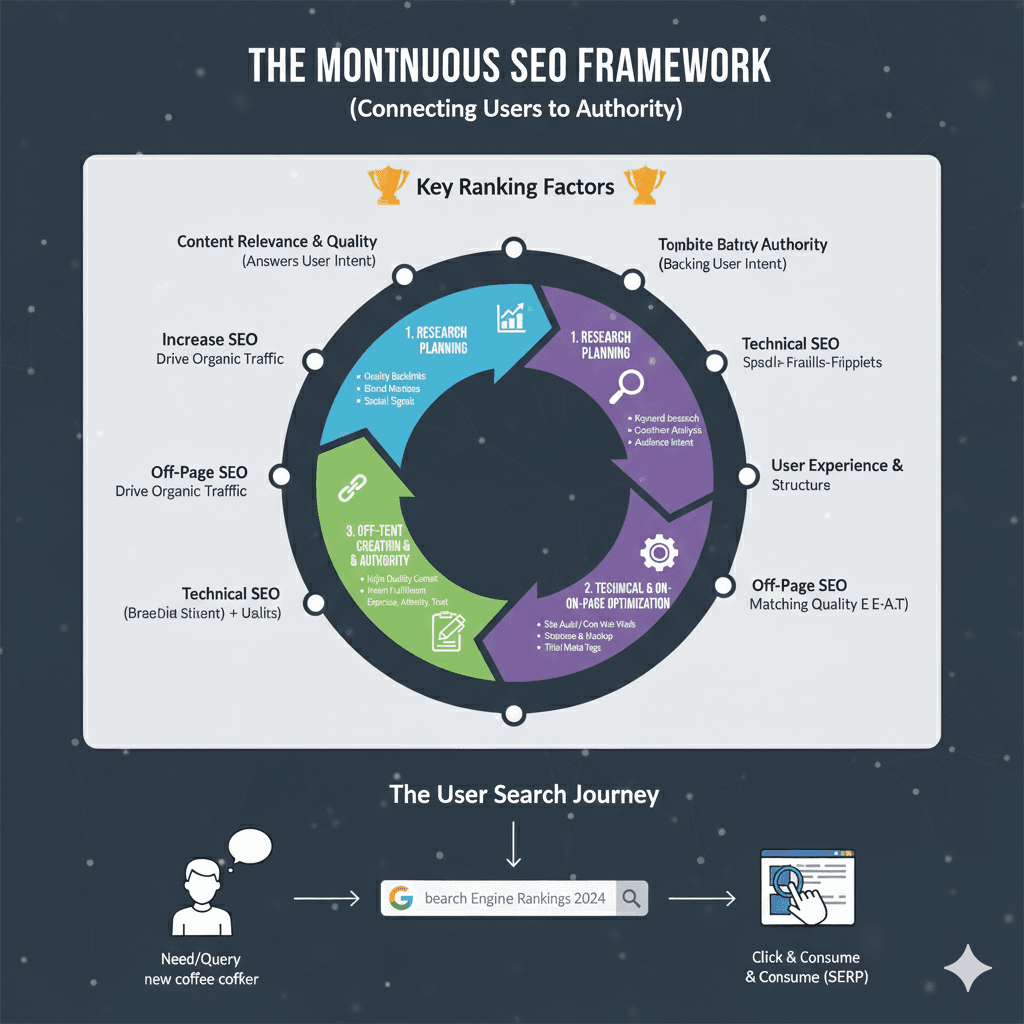
What is SEO? Getting Found Online.
The graphic places the definition of SEO at the center and uses radiating branches to explain different facets of the concept.
1. Core Goals and Outcomes
- Increased Organic Traffic Traffic & Conversions: The ultimate business objective of SEO.
- Increase Visibility, Enabling: Making a website easier to find by potential users.
- Increase SEO Drive Organic Traffic: Highlighting that the effort is aimed at growing unpaid traffic.
- Drive Growlts: Implies SEO is a driver of business growth.
2. SEO Components (How It Works)
- Technical SEO: Includes optimizing for Mobels (Mobile) and conversions.
- Off-Page SEO: Focuses on external validation, specifically Matching Quality and E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trust).
- Content Link Bulling E-E-A-T: Emphasizes that high-quality content and building external links are essential for demonstrating authority.
- On-Page SEO: Involves optimizing elements directly on the website to drive organic traffic and better serve users.
3. Connecting Users to Solutions (The Value Proposition)
- User Action: A user searches for a solution (“I need tralps a new coffee maker”).
- SEO Goal: SEO acts as the connector (“SEO: Connecting Usertas Users to YOUR Solutions”).
- Result: The goal is to match the user with a Website with need Conversions (a site that fulfills their need and converts them into a customer).
Related Articles from Our Network
- Jackson JSON Parser: A Comprehensive Guide to Parse JSON for Java Developers(json parser)
- python jwt: How to Securely Implement jwt in python(json web token)
- Mastering the Dummy API Response: Your Guide to Dummy API Development and Reqres(fake json)
- How to Effectively Use a JSON Comparator Online: Your Ultimate Guide to JSON Compare, and JSON Diff(compare json)