Search Engine Optimization: Mastering the Search Engine for SEO Success
Understanding Search Engines: The Cornerstone of SEO
In today’s digital landscape, having a website isn’t enough; it needs to be discoverable. This is where the search engine comes into play. A search engine is a software system designed to carry out web searches, which means to search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a textual web search query. For any business or individual aiming for an online presence, understanding Search Engine Optimization (SEO) for optimal performance is absolutely crucial for SEO success on Google, Bing, and alternative engines like DuckDuckGo and Qwant.
This guide will demystify the inner workings of the search engine and provide actionable strategies to help your content rank higher in search results and attract more organic traffic.
How Search Engines Work: The Core Mechanics
Before you can optimize for search engines, you need to understand their fundamental processes. While each search engine has its unique algorithms, the core operations remain consistent. This knowledge is key to effective search optimization.
1. Crawling: Discovering Web Pages
Search engines use automated programs, often called ‘spiders’ or ‘crawlers’, to scour the internet and find new or updated web pages.
- Sitemaps: Submit an XML sitemap to search engines (e.g., via Google Search Console) to provide them with a comprehensive list of all pages you want indexed.
- robots.txt: This file tells crawlers which parts of your site they can or cannot access.
2. Indexing: Organizing Information
Once a crawler finds a page, the search engine processes and analyzes its content, categorizing and storing it in a massive database called the ‘index’. If a page isn’t in the index, it cannot appear in search results.
- Quality Content: Focus on creating high-quality, relevant, and unique content that provides value to users.
- Canonicalization: Use canonical tags to tell search engines the preferred version of a page when duplicate content exists.
3. Ranking: Presenting the Best Results
- Relevance: How closely does the content match the user’s query?
- Authority: How trustworthy and credible is the website and specific page? This is a key factor in SEO rankings.
How to Optimize Your Content for Search Engines
Now that you understand the mechanics, let’s dive into practical SEO strategies for effective search optimization.
1. Keyword Research: The Foundation
- Long-Tail Keywords: Focus on longer, more specific phrases to capture highly targeted traffic.
- User Intent: Categorize keywords by informational, navigational, or transactional intent to create content that directly answers user needs.
2. On-Page SEO: Optimizing Your Content
- Title Tags: Craft compelling and keyword-rich title tags that accurately describe your page’s content.
- Meta Descriptions: Write concise and persuasive meta descriptions that entice users to click.
- Headings (H1, H2, H3): Use headings to structure your content logically and include keywords naturally.
3. Technical SEO: Ensuring a Healthy Website
- Site Speed: Optimize loading times.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure your website is responsive.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): Implement schema markup to provide search engines with more context about your content.
4. Off-Page SEO: Building Authority
- Backlinks: Acquire high-quality backlinks from reputable and relevant websites.
- Search Ads and Marketing: While SEO focuses on organic results, running well-targeted search ads can boost visibility and inform your SEO marketing strategy.
- Brand Mentions: Cultivate your brand’s presence across the web, including social media and industry forums.
🧭 The Rise of Private Search Engines: DuckDuckGo and Qwant
While Google dominates the market, the landscape is evolving. Private search engines like DuckDuckGo and Qwant are gaining popularity among users who prioritize data privacy and avoid tracking.
| Search Engine | Focus | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Google Search | Comprehensive Results | Market Share, Vast Index |
| DuckDuckGo Search | Private Search | No User Tracking |
| Qwant | European Engine, Privacy | Unbiased Results, Media Focus |
Conclusion: Empower Your Online Presence
Mastering the search engine for SEO is not a one-time task but an ongoing process of search optimization. By understanding their mechanics and implementing consistent optimization strategies, referencing SEO Google best practices and alternative engines, you can significantly enhance your website’s visibility, attract more qualified traffic, and ultimately achieve your online goals. Start applying these principles today and watch your online presence grow!
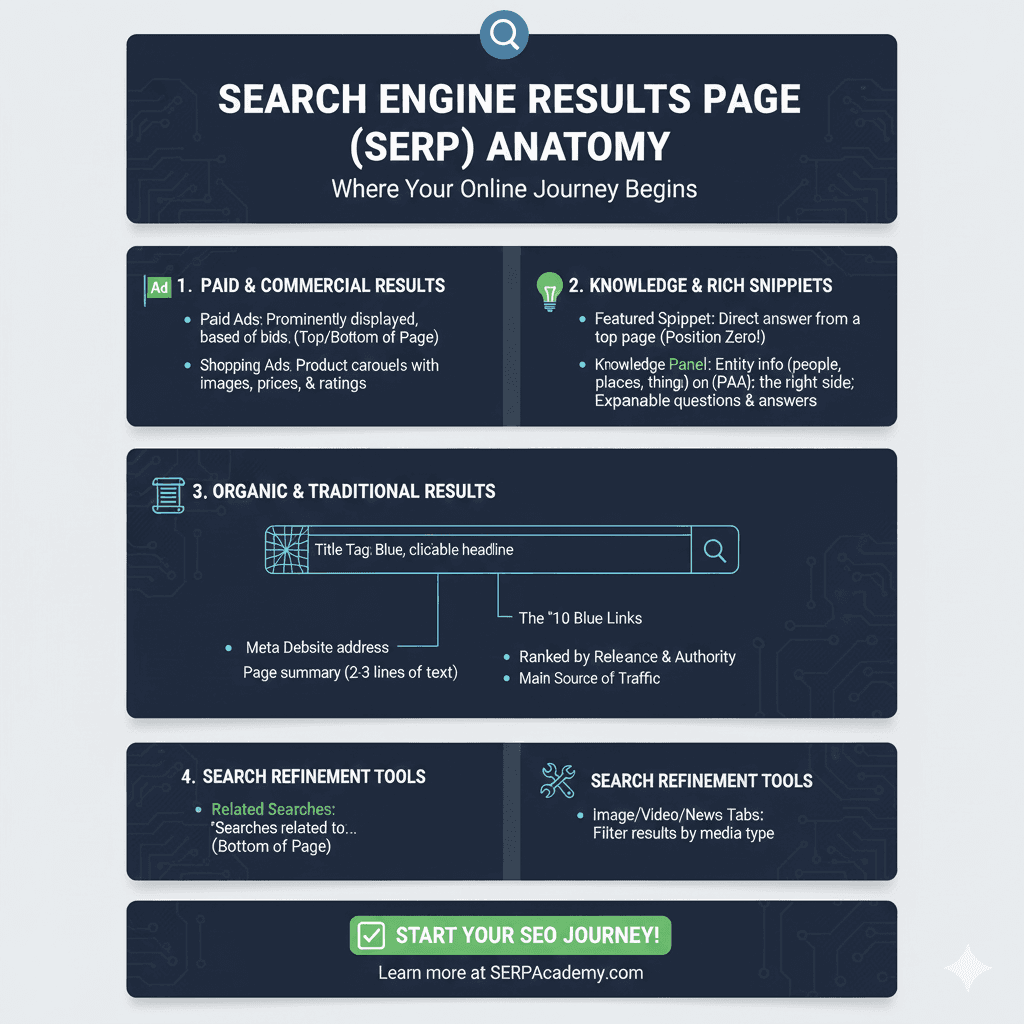
SERP Anatomy
This infographic details the various sections of a Search Engine Results Page (SERP), which is the final output a user sees after performing a query.
1. Paid & Commercial Results 💰
- Paid Ads: Prominently displayed and based on bids, often found at the top and bottom of the page.
- Shopping Ads: Product carousels that display product images, prices, and ratings.
2. Knowledge & Rich Snippets 🧠
- Featured Snippet: A direct answer pulled from a top-ranking page, placed at Position Zero.
- Knowledge Panel: An information box detailing entity info (people, places, things) or People Also Ask (PAA) expandable questions and answers.
3. Organic & Traditional Results 📜
- The “10 Blue Links”: The main body of the results, ranked by relevance and authority. These are the main source of traffic.
- Title Tag: The blue, clickable headline of the search result.
- Meta Description: A page summary, typically 2-3 lines of text, displayed below the title.
4. Search Refinement Tools 🛠️
- Related Searches: Suggestions for searches related to the current query, usually found at the bottom of the page.
- Image/Video/News Tabs: Tabs that allow the user to filter results by media type.