How to Master a Search Engine Optimization: Your Ultimate Guide
In today’s digital landscape, having a stunning website is only half the battle. If your target audience can’t find you, then even the most beautifully designed site won’t achieve its full potential. This is where a search engine optimization (SEO) comes into play. It’s the art and science of improving your website’s visibility when people search for products or services related to your business on Google, Bing, and other search engines.
This guide will walk you through the essential steps and strategies on how to effectively implement SEO to drive more organic traffic to your site and ensure it stands out from the competition.
What is a Search Engine Optimization and Why Does It Matter?
At its core, a search engine optimization is about making your website more appealing to search engines. When search engines like Google crawl the web, they look for specific signals to determine the relevance and authority of your content. A well-optimized site ranks higher in search results, meaning more visibility, more clicks, and ultimately, more potential customers.
Key Benefits of Strong SEO:
- Increased Organic Traffic: Attract users who are actively searching for what you offer.
- Improved Credibility & Trust: High rankings often equate to perceived authority.
- Better User Experience: SEO encourages a well-structured and fast website.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Organic traffic can be more sustainable than paid advertising.
How to Implement a Search Engine Optimization: Practical Steps
1. Keyword Research: The Foundation of SEO
Before you write a single line of content, you need to understand what your audience is searching for. Keyword research identifies the terms and phrases people use when looking for information, products, or services relevant to your business.
How to do it:
- Use tools like Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, or Ubersuggest.
- Look for keywords with a good balance of search volume and reasonable competition.
- Consider long-tail keywords (e.g., “best vegan restaurants in Brooklyn”) which are more specific and often have higher conversion rates.
2. On-Page SEO: Optimizing Your Content
On-page SEO refers to all the optimizations you can perform directly on your website pages to improve their search engine ranking.
Key Elements:
- Title Tags: Include your primary keyword, ideally at the beginning. Keep them concise (50-60 characters).
- Meta Descriptions: A compelling summary (150-160 characters) that encourages clicks. Include your keyword.
- Header Tags (H1, H2, H3): Structure your content logically. Your H1 should contain your main keyword.
- High-Quality Content: Provide valuable, comprehensive, and unique content that answers user queries.
- Keyword Density & LSI Keywords: Don’t stuff keywords. Use them naturally and incorporate Latent Semantic Indexing (LSI) keywords (synonyms and related terms).
- Image Optimization: Use descriptive filenames and alt text for images.
- Internal Linking: Link relevant pages within your website to each other.
3. Technical SEO: Ensuring Your Site is Search Engine Friendly
Technical SEO focuses on website and server optimizations that help search engine spiders crawl and index your site more effectively.
Crucial Aspects:
- Site Speed: A fast-loading website is crucial for user experience and rankings. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure your site is responsive and provides a seamless experience on all devices.
- XML Sitemaps: Help search engines discover all your important pages.
- Robots.txt: Directs search engine bots on which pages to crawl or ignore.
- SSL Certificate (HTTPS): A secure website (HTTPS) is a ranking factor and builds trust.
- Structured Data (Schema Markup): Helps search engines understand the context of your content, potentially leading to rich snippets.
Example robots.txt to disallow /admin/ directory:
User-agent: * Disallow: /admin/
4. Off-Page SEO: Building Authority and Trust
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your website to impact your search engine rankings. The primary component is backlinks.
Effective Strategies:
- Backlink Building: Acquire high-quality backlinks from reputable websites. This signals authority to search engines.
- Guest Blogging: Write for other relevant blogs to earn backlinks and expand your reach.
- Social Media Marketing: While not a direct ranking factor, social signals can increase content visibility and lead to more natural backlinks.
- Brand Mentions: Unlinked mentions of your brand can still contribute to your authority.
Measuring Your SEO Success
Implementing a search engine optimization is an ongoing process. You need to monitor your progress to understand what’s working and what needs adjustment.
Tools to Use:
- Google Analytics: Track organic traffic, user behavior, conversions.
- Google Search Console: Monitor your site’s search performance, index status, and identify crawl errors.
- Rank Tracking Tools: Keep an eye on your keyword rankings.
Conclusion
Mastering a search engine optimization is a journey, not a destination. By consistently applying the “how to” strategies outlined in this guide – from meticulous keyword research and on-page optimizations to technical upkeep and robust backlink building – you’ll significantly improve your website’s visibility and attract a steady stream of targeted organic traffic. Stay updated with algorithm changes, continue to provide value to your audience, and watch your search rankings soar!
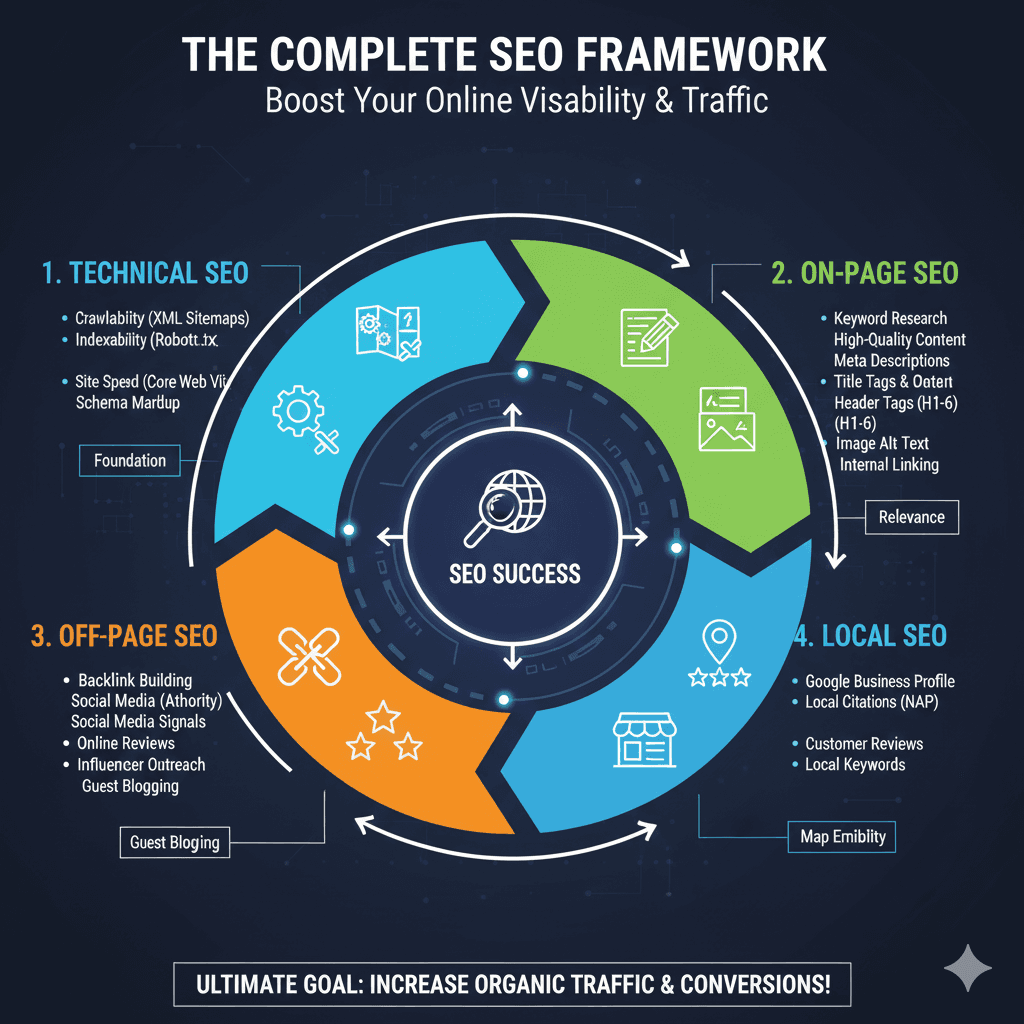
📈 The Complete SEO Framework
The image is an infographic titled “THE COMPLETE SEO FRAMEWORK: Boost Your Online Visibility & Traffic”. It outlines a cyclical framework for achieving SEO Success by breaking the strategy down into four major components: Technical SEO, On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO, and Local SEO.
1. Technical SEO (Foundation)
This is the base of the framework, ensuring the site is accessible to search engines.
- Crawlability (XML Sitemaps)
- Indexability (Robots.txt)
- Site Speed (Core Web Vitals)
- Schema Markup
2. On-Page SEO (Relevance)
This component ensures the content is highly relevant to user searches.
- Keyword Research
- High-Quality Content
- Meta Descriptions
- Title Tags & Header Tags (H1-H6)
- Image Alt Text
- Internal Linking
3. Off-Page SEO (Guest Blogging)
This focuses on building authority and trust from external sources.
- Backlink Building
- Social Media (Authority & Signals)
- Online Reviews
- Influencer Outreach
- Guest Blogging
4. Local SEO (Map Eligibility)
This is crucial for businesses targeting a specific geographic area.
- Google Business Profile
- Local Citations (NAP: Name, Address, Phone)
- Customer Reviews
- Local Keywords
Related Articles from Our Network
- How to Parse JSON in C#: A Comprehensive Guide with Examples(json parser)
- Auth0 JWT Token: How to Integrate and Verify JWT Tokens in Your Application(json web token)
- How to Supercharge Your Web Development with Dummy JSON APIs(fake json)
- Compare Two JSON Files-Mastering the JSON Compare Tool for Developers(compare json)