How to Boost Your SEO Rank: A Comprehensive Guide
In today’s digital landscape, having a strong online presence is non-negotiable for businesses and content creators alike. A key component of this presence is your website’s SEO rank. But what exactly is SEO rank, and more importantly, how can you improve it?
This guide will walk you through actionable strategies and best practices to help you understand, enhance, and maintain a high SEO rank, driving more organic traffic and achieving your online goals.
Understanding SEO Rank: What It Is and Why It Matters
Your SEO rank refers to the position your website or a specific web page appears in search engine results pages (SERPs) for particular keywords. When someone searches for a query, search engines like Google use complex algorithms to determine which pages are most relevant and authoritative, and thus, where they should rank.
Why a High SEO Rank is Crucial
- Increased Visibility: Pages ranking on the first page, especially in the top three positions, receive the vast majority of clicks.
- More Organic Traffic: A higher rank directly translates to more free, targeted traffic to your site.
- Enhanced Credibility and Trust: Users often perceive higher-ranked sites as more authoritative and trustworthy.
- Higher Conversion Rates: Organic traffic tends to have a higher conversion rate because users are actively searching for solutions your content or product might provide.
1. Master Keyword Research
Keyword research is the cornerstone of any successful SEO strategy. It involves identifying the words and phrases your target audience uses when searching for information related to your business or content.
Identify High-Intent Keywords
- Short-Tail vs. Long-Tail Keywords: Balance broad terms (e.g., “SEO tips”) with more specific, longer phrases (e.g., “how to improve local SEO rank for small business”) that often have lower competition and higher conversion potential.
- Competitor Analysis: Analyze what keywords your competitors are ranking for. Tools like SEMrush or Ahrefs can reveal valuable insights.
- Use Keyword Research Tools: Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush, and Ubersuggest can help you discover new keywords, analyze their search volume, and evaluate competition.
Understand Searcher Intent
Keywords aren’t just about words; they’re about the intention behind the search. Categorize keywords by intent:
- Informational: Users looking for answers or general information (e.g., “what is SEO?”).
- Navigational: Users looking for a specific website or brand (e.g., “Google Maps”).
- Transactional: Users ready to buy (e.g., “buy SEO software”).
- Commercial Investigation: Users researching before making a purchase (e.g., “best SEO tools 2024”).
2. Optimize Your On-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to all the optimizations you can perform directly on your website to improve its ranking factors.
Title Tags and Meta Descriptions
- Include your primary keyword naturally.
- Keep title tags concise (50-60 characters) and meta descriptions compelling (150-160 characters).
- Make them accurately describe the page content.
- <title>How to Boost Your SEO Rank: A Comprehensive Guide</title>
High-Quality, Engaging Content
- Provide in-depth answers to user queries.
- Break up text with headings, subheadings, lists, and images for readability.
- Keep content fresh and updated.
- Aim for unique insights and value.
Header Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.)
- Use only one H1 tag per page, ideally including your primary keyword.
- Use H2s for main sections and H3s for subsections.
- Integrate relevant keywords naturally within your headers.
Image Optimization
- Compress images to reduce file size without sacrificing quality.
- Use descriptive filenames (e.g., how-to-improve-seo-rank.jpg).
- Fill in alt text with a clear description, including keywords where appropriate. This helps search engines understand the image content and improves accessibility.
URL Structure
- Use hyphens to separate words.
- Keep URLs short and descriptive (e.g., www.example.com/how-to-boost-seo-rank).
- Avoid long strings of numbers or irrelevant characters.
3. Implement Technical SEO Best Practices
Technical SEO focuses on website and server optimizations that help search engine spiders crawl, index, and render your site more effectively.
Site Speed and Performance
- Optimize images and videos.
- Leverage browser caching.
- Minimize CSS, JavaScript, and HTML.
- Use a Content Delivery Network (CDN).
- Choose a reliable hosting provider.
Mobile-Friendliness
- Ensure your website design adapts to all screen sizes.
- Test your site’s mobile-friendliness using Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
XML Sitemaps and Robots.txt
- XML Sitemaps: Help search engines discover all important pages on your site. Submit yours via Google Search Console.
- Robots.txt: Instructs search engine crawlers which pages or sections of your site they should or should not access.
- User-agent: *
- Disallow: /wp-admin/
HTTPS Security
HTTPS (Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure) encrypts communication between the user’s browser and your website. It’s a ranking signal and essential for user trust.
- Ensure your site has an SSL certificate.
Structured Data Markup (Schema Markup)
Schema markup helps search engines understand the context of your content, leading to rich snippets in SERPs, which can improve CTR.
- Use Schema.org vocabulary to mark up elements like reviews, recipes, events, and products.
4. Build a Robust Backlink Profile
Backlinks (incoming links from other websites) are a critical ranking factor. They signal to search engines that other sites vouch for your content’s authority and relevance.
Quality Over Quantity
One backlink from a high-authority, relevant website is far more valuable than dozens from low-quality or spammy sites.
Strategies for Earning Backlinks
- Create High-Quality, Link-Worthy Content: Develop comprehensive guides, original research, or compelling infographics that others naturally want to link to.
- Guest Posting: Write articles for other reputable websites in your niche, including a link back to your site.
- Broken Link Building: Find broken links on other websites and suggest your content as a replacement.
- Content Promotion: Share your content on social media, reach out to influencers, and email relevant contacts to generate visibility and potential links.
- Competitor Backlink Analysis: Analyze your competitors’ backlinks to identify potential linking opportunities.
5. Enhance User Experience (UX)
Google increasingly prioritizes websites that offer a positive user experience. UX signals contribute to your SEO rank.
Core Web Vitals
- Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Measures loading performance.
- First Input Delay (FID): Measures interactivity.
- Layout Shift (CLS): Measures visual stability.
Aim to meet Google’s thresholds for these metrics, which you can monitor in Google Search Console.
Intuitive Navigation
Make it easy for users to find what they’re looking for with clear menus, internal links, and a logical site structure.
Engage Your Audience
- Use compelling calls to action.
- Embed videos or interactive elements.
- Encourage comments or discussions.
6. Monitor and Analyze Your Performance
SEO is not a set-it-and-forget-it strategy. Continuous monitoring and analysis are essential for long-term success and to adapt to algorithm changes.
Utilize SEO Tools
- Google Analytics: Track website traffic, user behavior, and conversions.
- Google Search Console: Monitor your site’s performance in search results, identify crawling errors, and submit sitemaps.
- SEMrush/Ahrefs/Moz: Advanced tools for keyword research, competitor analysis, backlink monitoring, and site audits.
Track Key Metrics
- Keyword Rankings: Monitor the position of your target keywords in SERPs.
- Organic Traffic: Track the volume of visitors coming from search engines.
- Bounce Rate: The percentage of visitors who leave your site after viewing only one page.
- Conversion Rates: Measure how many visitors complete a desired action (e.g., purchase, form submission).
- Core Web Vitals: Regularly check and improve your site’s performance metrics.
Conclusion
Boosting your SEO rank is a multifaceted journey that requires patience, continuous effort, and a willingness to adapt. By focusing on comprehensive keyword research, optimizing your on-page and technical SEO, building a strong backlink profile, enhancing user experience, and regularly monitoring your performance, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility in search results.
Remember, the goal of search engines is to provide the best possible results to their users. By prioritizing quality, relevance, and user experience, you align your strategy with theirs, paving the way for sustainable SEO success and a higher rank.
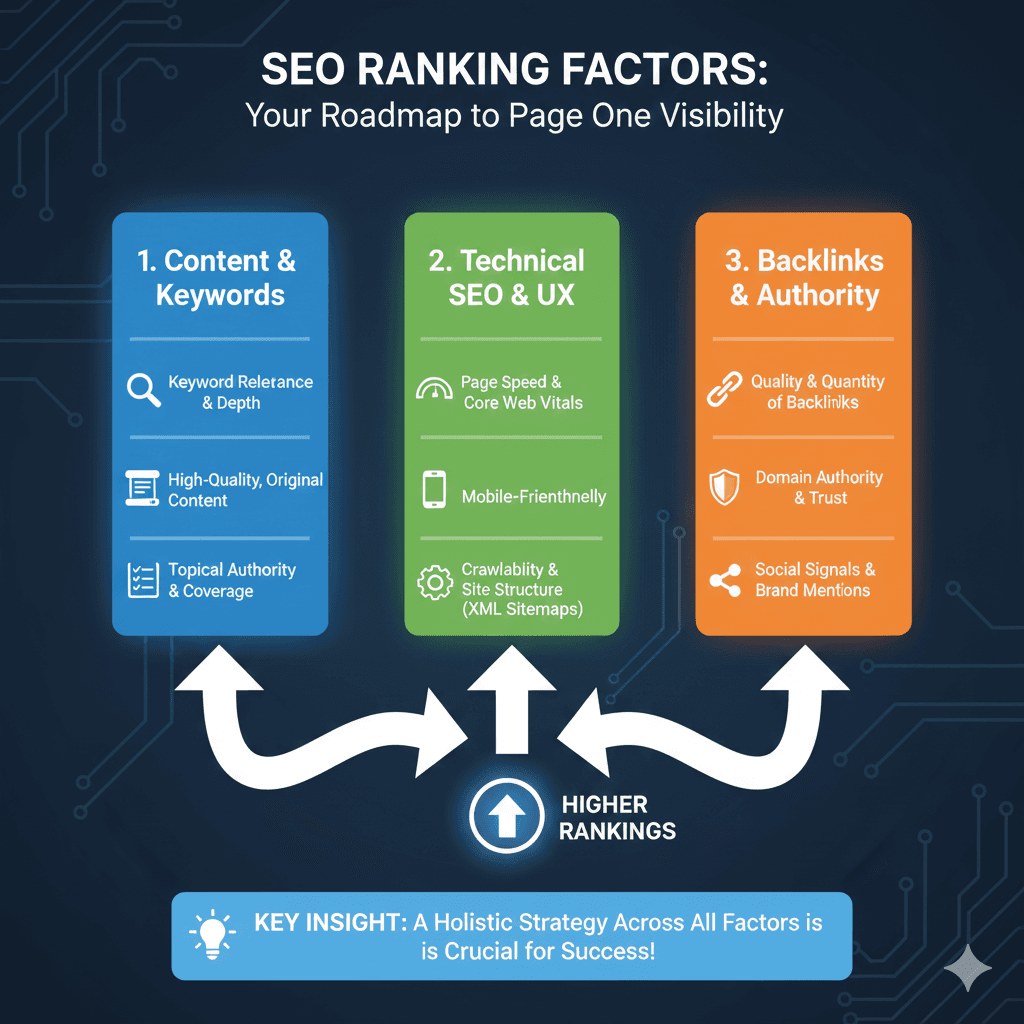
SEO Ranking Factors: Roadmap to Success
The infographic breaks down SEO success into three critical categories:
- Content & Keywords (Blue):
- Keyword Relevance & Depth: Ensuring your content matches the search intent of your target audience.
- High-Quality, Original Content: Creating unique value that search engines prioritize over duplicated material.
- Topical Authority & Coverage: Demonstrating expertise by thoroughly covering a subject area.
- Technical SEO & UX (Green):
- Page Speed & Core Web Vitals: Optimizing how fast your site loads and its overall visual stability.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensuring your site is fully functional and easy to navigate on smartphones and tablets.
- Crawlability & Site Structure: Using tools like XML sitemaps to help search engines easily find and index your pages.
- Backlinks & Authority (Orange):
- Quality & Quantity of Backlinks: Earning links from other reputable websites to act as “votes of confidence.”
- Domain Authority & Trust: Building a long-term reputation for reliability and relevance in your industry.
- Social Signals & Brand Mentions: Monitoring how often your brand is discussed and shared across social platforms.
Related Articles from Our Network
- WHAT IS API JSON Parser – JSON Parser API – JSON.parse(json parser)
- WHAT IS JWT Security, Web Security,-JSON Web Tokens(json web token)
- What is Dummy JSON Data- Free Fake Rest Api JSON Data(fake json)
- JSONCompare: The Ultimate JSON Compare Tool(compare json)