What is SEO? An Introduction to Search Engine Optimization
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, is the practice of increasing the quantity and quality of traffic to your website through organic search engine results. It’s about understanding what people are searching for online, the answers they are looking for, the words they’re using, and the type of content they wish to consume.
Ultimately, SEO aims to make your website more visible to search engines like Google, Bing, and Yahoo, so when users search for topics relevant to your business or content, your site ranks higher on the Search Engine Results Pages (SERPs). This increased visibility means more potential customers or readers find their way to your site.
Why is SEO Important for Your Business?
- Increased Organic Traffic: Higher rankings lead to more clicks and visitors without paying for ads.
- Credibility and Trust: Websites ranking high are often perceived as more credible and trustworthy by users.
- Better User Experience: SEO encourages practices that improve site speed, mobile-friendliness, and easy navigation.
- Cost-Effectiveness: While not free, organic traffic can be a more sustainable and cost-effective long-term strategy compared to continuous paid advertising.
- Market Share: Dominate your niche by appearing for a wide range of relevant search terms.
How to Do SEO: A Step-by-Step Guide to Boosting Your Rankings
Now that we understand what SEO is and why it’s crucial, let’s dive into the practical steps on how to implement an effective SEO strategy for your website.
1. Keyword Research
Keyword research is the foundation of any successful SEO campaign. It involves identifying the words and phrases your target audience uses when searching for information related to your products, services, or content.
- Identify Seed Keywords: Start with broad terms related to your business.
- Analyze Search Volume & Competition: Use tools (e.g., Google Keyword Planner, Ahrefs, SEMrush) to find keywords with good search volume but manageable competition.
- Understand User Intent: Categorize keywords by informational, navigational, transactional, or commercial investigation intent.
- Long-Tail Keywords: Don’t overlook longer, more specific phrases (e.g., “best vegan restaurant in Brooklyn”) as they often have lower competition and higher conversion rates.
2. On-Page SEO
On-page SEO refers to all the optimizations you can make directly on your website pages to improve their search engine rankings. This includes both content and HTML source code.
- Title Tags: Create unique, compelling, and keyword-rich title tags for every page (under 60 characters).
- Meta Descriptions: Write descriptive and enticing meta descriptions (around 150-160 characters) that include your primary keywords and encourage clicks.
- Header Tags (H1, H2, H3): Structure your content with clear headings. Use one H1 tag per page for your main topic, and H2s and H3s for subheadings.
- High-Quality Content: Create valuable, original, and comprehensive content that genuinely helps your audience and naturally incorporates your keywords.
- Image Optimization: Use descriptive file names and alt text for images to help search engines understand their context.
- Internal Linking: Link relevant pages within your website to each other to improve navigation and distribute link equity.
3. Technical SEO
Technical SEO ensures that search engine crawlers can efficiently access, crawl, interpret, and index your website. It deals with website and server optimizations.
- Site Speed: Optimize images, leverage browser caching, and minify CSS/JavaScript to ensure fast loading times.
- Mobile-Friendliness: Ensure your website is responsive and provides an excellent experience on all devices.
- XML Sitemaps: Submit an XML sitemap to Google Search Console to help search engines discover all your important pages.
- Robots.txt: Use this file to instruct search engine bots which parts of your site they should or shouldn’t crawl.
- SSL Certificate (HTTPS): Secure your website with an SSL certificate; it’s a ranking factor.
- Canonical Tags: Use canonical tags to prevent duplicate content issues.
4. Off-Page SEO (Link Building)
Off-page SEO refers to actions taken outside of your own website to impact your rankings within search engine results pages. The primary component of off-page SEO is link building.
- Backlinks: Acquire high-quality backlinks from authoritative and relevant websites. These act as “votes of confidence” for your site.
- Guest Blogging: Write articles for other websites in your niche to earn backlinks and establish authority.
- Broken Link Building: Find broken links on other sites and suggest your content as a replacement.
- Social Media Marketing: While social signals aren’t direct ranking factors, they can drive traffic and increase content visibility, leading to more shares and potential backlinks.
5. Content Creation
Content is king in SEO. Regularly creating fresh, high-quality, and relevant content that addresses user intent is vital for attracting and retaining visitors.
- Address User Intent: Create content that directly answers the questions or fulfills the needs of your target audience.
- Long-Form Content: Often ranks better because it tends to be more comprehensive and provides more value.
- Content Diversity: Experiment with different formats like blog posts, videos, infographics, case studies, and guides.
- Update & Refresh: Regularly update old content to keep it current and relevant, signaling to search engines that your site is active and authoritative.
6. Monitoring and Analysis
SEO is an ongoing process. It’s crucial to monitor your performance and adapt your strategies based on data.
- Google Analytics: Track website traffic, user behavior, conversions, and more.
- Google Search Console: Monitor your site’s performance in Google search results, identify crawling errors, and submit sitemaps.
- Rank Tracking: Keep an eye on your keyword rankings to see how your efforts are impacting visibility.
- Competitor Analysis: Regularly analyze what your competitors are doing well and identify opportunities.
Basic HTML Example for On-Page SEO
Here’s a simple HTML structure demonstrating good on-page SEO elements:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Your Primary Keyword | Secondary Keyword Phrase</title>
<meta name="description" content="A concise, engaging meta description (150-160 chars) including your main keywords and a call to action.">
</head>
<body>
<h1>Main Topic: Your Primary Keyword Here</h1>
<p>Start your content here, naturally incorporating your target keywords. Make it valuable and readable.</p>
<h2>Related Subtopic with a Secondary Keyword</h2>
<p>Provide more detailed information. Use bullet points or lists for readability.</p>
<ul>
<li>Benefit One of Your Solution</li>
<li>Benefit Two of Your Solution</li>
</ul>
<h3>Another Specific Detail</h3>
<p>Further expand on relevant points.</p>
</body>
</html>By understanding what SEO is and meticulously applying these ‘how to’ steps, you can significantly improve your website’s visibility, attract more qualified traffic, and achieve your online business goals. Remember, SEO is a marathon, not a sprint, requiring continuous effort and adaptation to algorithm changes.
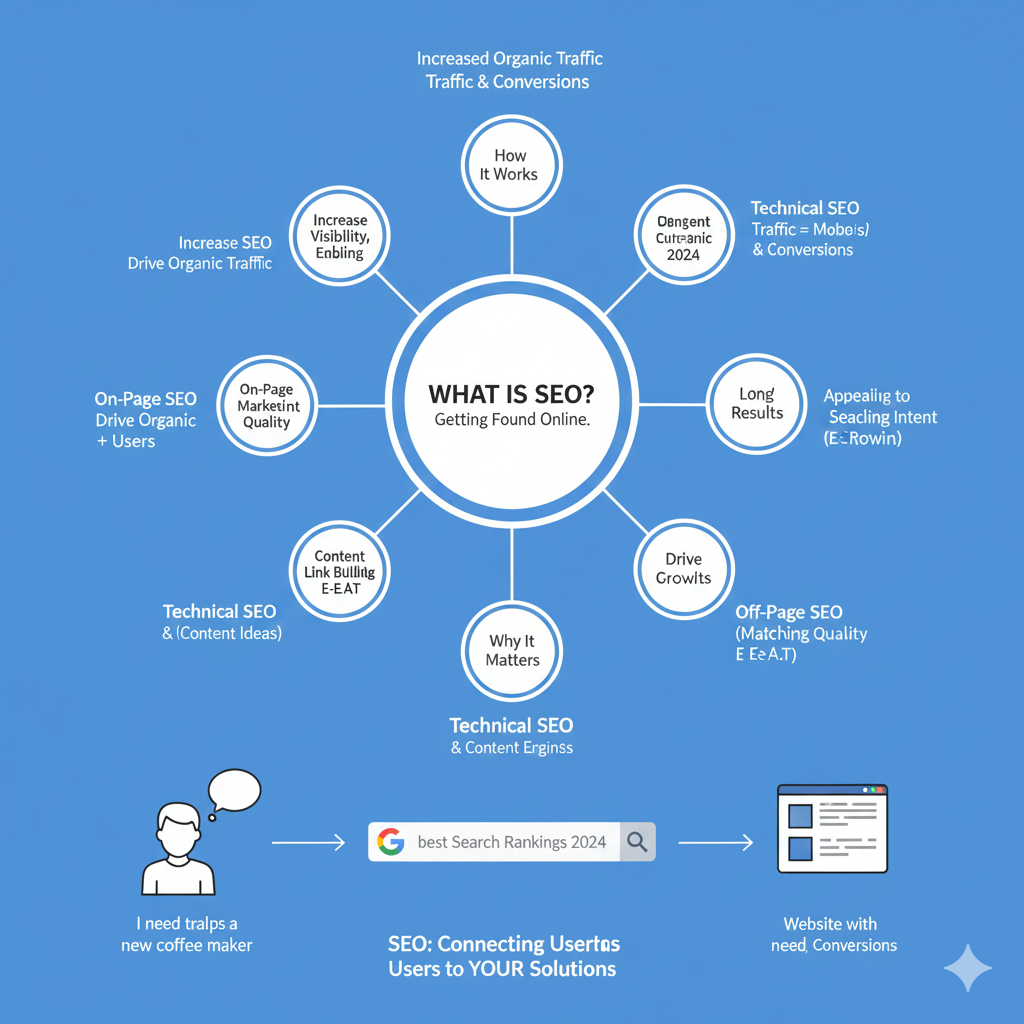
What is SEO? Getting Found Online.
The infographic centers around the definition of SEO and branches out to cover its goals, mechanics, and core strategies.
1. Core Goals and Outcomes
- Increased Organic Traffic Traffic & Conversions: The primary business goal of SEO.
- Increase Visibility, Enabling: Making the website visible to a broader audience.
- Increase SEO Drive Organic Traffic: SEO efforts are aimed at increasing traffic that is not paid for.
- Drive Growlts: Implies driving business growth.
2. SEO Components (How It Works)
The components are categorized by the area of optimization:
- Technical SEO: Includes aspects like site speed, mobile-friendliness (“Mobels”), and conversions.
- Off-Page SEO: Focuses on external signals like Matching Quality and E-E-A-T (Expertise, Experience, Authority, and Trust).
- Content Link Bulling E-E-A-T: Emphasizes that high-quality content and link building are crucial for demonstrating E-E-A-T.
- On-Page SEO: Involves optimizing elements directly on the website to drive organic traffic and users.
3. Connecting Users to Solutions (The Value Proposition)
The bottom of the infographic illustrates the core function of SEO:
- User Action: A user types a query (“I need tralps a new coffee maker”) into a search engine (labeled “best Search Rankings 2024”).
- SEO Goal: SEO acts as the bridge (“SEO: Connecting Usertas Users to YOUR Solutions”).
- Result: The goal is to match the user with a Website with need Conversions.
learn for more knowledge
Json parser -> BeautifulSoup JSON Parser-Combining BeautifulSoup and JSON for Web Scraping – json parse
Json web token ->How to Use com.auth0.jwt for Secure JWT Handling in Java – json web token
Json Compare ->JSON Comparator: The Ultimate Guide to JSON Compare Online and Offline Tools – online json comparator
Fake Json –>What Is JSON Mock API? (Beginner-Friendly Explanation) – fake api
Leave a Reply